Negative search engine marketing is the act of targeting competitor websites, attempting to negatively affect position in search results, reputation, click through rate or visibility online. The mentality is, “if you can’t beat em, hurt em” until your site begins to appear in results.
Negative SEO is generally viewed as taboo, few in the internet marketing industry condone or practice Negative SEO. Many articles discuss negative SEO from a prevention and backlink perspective, although there was a recent article from sempost.com on how it can even be accomplished without links.
To truly explain, we need to cover how it is typically implemented.
- Negative SEO typically involves black hat tactics (tactics that are better defined as “search engine manipulation”). Many black hat techniques are now penalized by Google’s algorithm filters. They include: building low quality and spammy backlinks to a competitor, generating thousands of comment links to a competitor, adding keyword rich anchor text (the text that is linked), and many more. Google doesn’t know if the website, their agency or their competitor is conducting the black hat techniques, so unfortunately the competitor is typically penalized.
- Negative SEO often targets sites that follow Google’s guidelines. Anyone who ranks near the first position, is at high risk of being a victim of negative SEO. Most applications of Negative SEO are therefore unethical.
- Negative SEO is viewed as a desperate measure since most businesses/agencies who implement it can’t rank themselves. It’s a last resort to take down those on top.
What is Ethical Negative SEO?
To summarize, most applications of negative SEO are unethical, targeting any site ranking towards the top, involving black hat techniques to discredit legitimate websites by desperate agencies or businesses.
In contrast, Ethical Negative SEO targets competition involved in black hat techniques, manipulating search results to appear at the top. These sites, while not yet penalized by Google are stealing traffic and customers from those who follow Google’s guidelines. Implementing these Google approved negative SEO tactics will hurt those engaged in black hat tactics and help your business.
We’ve all seen a website where upon closer analysis, it became clear the business purchased backlinks or earned authority in a way not compatible with Google’s guidelines. It’s frustrating to encounter competition outranking your own business, that don’t deserve to be so visible. They’ve cheated their way to getting website traffic and customers.
Negative SEO Tactic 1#: Google Map Corrections
Business Name Corrections
Because the name of a business still has strong weight in local rankings, many businesses disregard Google’s guidelines on the business name. Adding or in some cases, stuffing, keywords to the name, especially geographic terms, can get a businesses local map listing ranking quickly.
Recently, Google changed its guideline on descriptors in business name (great post on this topic here). Business names need to reflect the real world legal or doing business as name. This is often used to differentiate the business name from other locations such as Applebees North and Applebees South. However, many businesses take it overboard, violating Google’s guidelines.
Excerpt from full guidelines:
Cannot Be Used:
- Location information, such as neighborhood, city, or street name, unless it is part of the real-world representation of the business. Your name must not include street address or direction information.
- Not acceptable: “Starbucks Downtown“, “Macy’s Union Square“, “Holiday Inn (I-93 at Exit 2)“, “U.S. Bank ATM – 7th & Pike – Parking Garage Lobby near Elevator“
- Acceptable: “Starbucks”, “Macy’s”, “Holiday Inn Salem”, “U.S. Bank ATM”, “University of California Berkeley”
The problem with these guidelines, is Google doesn’t do their diligence in preventing businesses from stuffing keywords in their local listing name.
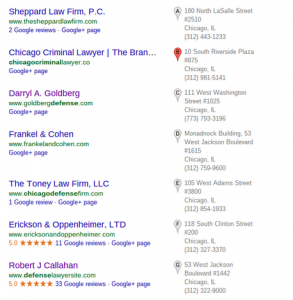
Before Local Pack with Spammed Listings
A screenshot of the local pack for “Chicago Criminal Defense Firms” features 5 businesses out of 7 that violate Google’s name guidelines.
Names:
- Robert J Callahan | Criminal Defense Lawyer
- Law Offices of David L. Freidberg, P.C.
- LAW OFFICE OF ANDREW WEISBERG – Criminal Defense Attorney
- Michael J. Petro | Chicago Criminal Defense Attorney
- Darryl A. Goldberg, CRIMINAL DEFENSE LAWYER
Can you spot the stuffed keyword? Criminal Defense Lawyer? 4 of the businesses have added the keyword or a close variation in order to rank in the local pack. You can always check the “Doing Business As” for the county, to check the official name of the business.
After you determined, the business is in fact, stuffing the name with a keyword phrase, submit a Google Maps correction report. Simply click on the Google Map listing then click “suggest an edit”. Cross out the incorrect name, adding the actual name of the business.
You can even add a note, although I wouldn’t recommend including anything about how the business is manipulating results. Simply add that the business isn’t using their legal name and has added a keyword phrase.
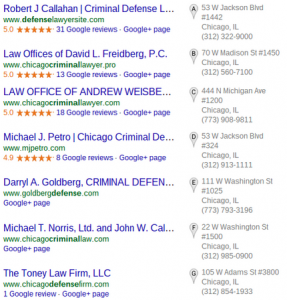
After Local Pack Spam Reported
 The local pack after submitting reports for all the law firms is very different. The Toney Law Firm moved up to position E, with a name that abided by Google’s guidelines in the previous screenshot. Robert J Callahan moved down from A to position G. There could be other factors involved, but without criminal defense lawyer next to his real law firm name, he lost position. Goldberg moved up to C from E, likely with the new mix of results. We can also see many new law firms, include a new local spammer, The Brandon Law Firm in position B. After reporting this firm for their name, the local pack is likely to follow Google’s local guidelines. Although with as big of a market as Chicago for criminal defense law firms, this will likely be a constant battle.
The local pack after submitting reports for all the law firms is very different. The Toney Law Firm moved up to position E, with a name that abided by Google’s guidelines in the previous screenshot. Robert J Callahan moved down from A to position G. There could be other factors involved, but without criminal defense lawyer next to his real law firm name, he lost position. Goldberg moved up to C from E, likely with the new mix of results. We can also see many new law firms, include a new local spammer, The Brandon Law Firm in position B. After reporting this firm for their name, the local pack is likely to follow Google’s local guidelines. Although with as big of a market as Chicago for criminal defense law firms, this will likely be a constant battle.
Business Address Corrections
Submit a Google Maps correction for virtual offices. If you have a good idea of your competition’s physical locations, but spot an odd competitor that you think may not have a physical presence in your city, submit a correction.
Virtual offices violate Google’s local guidelines. Confirm it is a virtual office by searching for the competitor’s address in Google Maps. Do multiple business show up for the same address? Many virtual offices will have office space, executive offices, or even virtual offices in their name and will appear on top of their clients in maps.
Simply suggest an edit, crossing out the address and add a note that you visited the business at the address, but it wasn’t there. It’s even more effective if you can get a few colleagues at different periods in a month to report a businesses address.
Both business address and name corrections will be reviewed quickly by editors within 72 hours. Google will even send you an email on whether your correction was accepted or rejected! So get to it.
Negative SEO Tactic 2#: Steal Exact Match Domain Traffic
It’s unfortunate Google hasn’t released an effective exact match domain penalty. One of the most frustrating areas of doing ethical SEO is seeing exact match domains with few backlinks, low quality content and questionable business models outranking legitimate sites.
However, you can also capitalize on EMD’s, but implement it as a defense strategy. At a minimum, you shouldn’t be ignorant of domains available for auction in your space. You should also own several of these domains and consider the practice of domain flipping. Keep the domain from competition, but if a news site or a non-competitive entity is seeking the domain, sell and profit from the sale. You will also profit by preventing the domain from being snatched by competitors.
One of the biggest downsides to using an exact match domain is low brand equity. For example, the attorney’s law office is really the name of the business, yet chicagocriminallawyers.com is the domain. Which do you think customers remember as the name of the business?
Create more brand confusion by purchasing the singular or plural form of the domain, essentially domain variations of the competitor you are attempting to hurt. Throw up a microsite landing page with unique content about your business.
Over time, your close domain variation will begin to rank. You will also capture direct traffic from any customer that forgets to add an S or types in chicagodefenseattorneys.com forgetting it’s chicagodefenselawyers.com. In even more competitive industries, you may find competitors are using hyphens (a poor and ineffective way) to stuff keywords in the domain. Watch the non-hyphen domain closely and if goes up for sale, buy it and cause even more confusion.
I’ve identified a company that has implemented this tactic effectively. They have created multiple microsites with unique content on each page and have even built links to these microsites, leveraging them to boost their main domain’s authority.
Main Site: datavox.net
Microsites
- http://www.houstonvoip.net/
- http://houstontelephonesystems.com/
- http://houstoncabling.net/
- http://houstoncisco.tel/
With your network of similar looking exact match domain microsites, you can now cheaply bid on the keywords in the domain using Google Adwords. Since the domain is so generic, the business cannot prevent you from bidding on their domain keywords, because they won’t be trademarked and will always be popular keywords. You’ll also benefit from having a higher quality score and can spend less of advertisements.
Now go out and steal that well deserved traffic!
Negative SEO Tactic 3#: Submitting Google Webspam Reports
This last tactic has the longest wait for a return. Matt Cutts originally unveiled the ability to submit webspam reports in Google Webmaster Tools back in 2010. Since then, it’s still indecisive whether all of these reports are read and acted upon. There are a variety of options, but essentially submitting a web spam report is Google’s system of reporting black hat activity.
The Categories:
- Paid Links – reporting activity seems like a black box, little action is taken
- Objectionable Content – inappropriate for non safesearch
- Malware – reports result in quick action
- Other Google Products
- Adsense, Google Maps, etc.
- Copyright and other legal issues – fast resolution
- Personal/Private
- Phishing – reports result in quick action
- Rich Snippets – you may find a competitor has added review schema in the wrong way, or used schema to unethically capture a higher click through rate. Report it and get it removed.
Most forms of black hat tactics fall into the paid links category which can be used to report link spam, paid links, traded links, etc. As suggested by Rand Fishkin in 2010, it is more likely that these reports help Google see what spam is getting through their algorithm filter, allowing them to fine tune and catch more webspam on the next algorithm refresh vs. sending out manual penalties. This would align with it being difficult to measure if sites reported to Google are overtime penalized.
Since the Penguin algorithm is confirmed to be released at a more regular update cycle, I would expect paid link reporting to become more effective. In 2013, during the initial penguin algorithm update, Matt Cutts even created a special Penguin spam report for submitting spam that wasn’t caught in the penguin algorithm filter. Whether this form is still being used for 2014 or beyond is unlikely.
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1rhRenrd16MDSgAOwnMVx9KQbp–0JoY9vKiJdIcMe44/viewform
Implementing ethical negative SEO should be viewed more as: tactics that negate, penalize and reduce visibility for competition engaged in black hat tactics. Too often, agencies and businesses rarely have time or the insight to prevent and combat the activities of competition. However, instead of cursing under your breath, take some proactive steps to protect your brand and position online with these easy to implement tactics.


 Corey is an independent digital consultant for agencies and clients throughout Texas. When he isn't thinking about the internet of things, he is a connoisseur of fine beer, traveling, indie music and is currently learning the bagpipes.
Corey is an independent digital consultant for agencies and clients throughout Texas. When he isn't thinking about the internet of things, he is a connoisseur of fine beer, traveling, indie music and is currently learning the bagpipes.

